Windows System Restore Point Guide
System Restore Overview & Guide Introduction
Windows System Restore is a very handy feature of Windows 7, Vista, Me and Windows XP operating systems that allow you to restore your computer’s Windows system files, registry, installed programs, etc. to an earlier point in time. Note: Using system restore does not restore your personal files such as photos, music, documents, etc.
This feature is especially useful if your system behaves unpredictably after say a major OS or driver update, or after installing a program, etc. If uninstalling the program, driver or update doesn’t solve your issue for example then system restore is a great last ditch effort to restore your computer to its previous working state.
What’s great about Windows System Restore is that by default a Windows system protection component regularly creates restore points for you so if you have to revert back to a previous state there are plenty of restore points to choose from. Of course you can also manually create your own restore points if you desire. If you are going to perform any new or questionable Windows maintenance, update, or installation etc. manually creating a restore point is a great peace of mind feature in the event something goes awry.
As you see Windows System Restore is a very nice Windows feature, just remember system restore is not intended as a file backup solution and so it does not help you recover a personal file that has been corrupted or deleted. Folks that are what regular data backups are for! :)
Of course in those unfortunate situations where Windows itself goes astray and you end up exhausting all your energy trying to resolve an issue with no avail, system restore is going to be an invaluable tool for it may just quickly get your system back up and running as it were before things went off track.
Windows System Restore Questions and Answers
So how does System Restore work?
System Restore uses automatically and manually created backups called restore points to restore your Windows system files and settings to an earlier point in time. Restore points are created automatically by Windows every week, and also before significant system changes such as program or driver installations. Manual restore points can also be created anytime by an end-user if desired. In a nutshell System Restore is a way to undo system changes to your computer without affecting your personal files, such as music, photos, and documents, etc.
Note: While system restore was not originally tied to user data in any way, in newer Windows operating systems such as Windows 7 Professional, system restore is tied to the `restore previous versions’ feature which is part of the Windows 7 System Protection component that controls both features. This `restore previous versions’ feature can give you the ability to restore some files and folders that you accidentally modified, deleted or even those that were damaged.
Tip: Continue to use a data backup solution despite this feature for it is not meant to replace ole school data backup.
Specifically what files are changed when I use Windows System Restore?
In Windows operating systems that support System Restore, System Restore primarily changes Windows system files, registry settings, and programs. System Restore can also change scripts, batch files and other executable files. “e.g.” If you install a new application on Saturday and then decide to restore your computer to a previous day’s restore point the application you installed on Saturday will be uninstalled.
Referring back to question one, System Restore does not change personal files. “e.g.” If you created a new Microsoft Word document on Saturday but restore you computer to say Tuesday or any previous day for that matter, your Microsoft Word doc file will still be on your computer in the same state as it were created on Saturday.
Note: If you use a newer Windows operating system such as Windows 7 you may be able to use the `restore previous versions’ feature that utilizes restore point to some degree, for it gives you limited ability to restore files to an older version or restore a deleted file.
What are the best practices when choosing a Windows System Restore Point?
Typically it is best to choose a restore point that was created right before the date and time you started noticing issues with your system. System Restore will automatically recommend the most recent restore point created before a significant system change was performed however you can also choose a restore point manually.
But in a nutshell, choose a restore point right before you noticed an issue. If you don’t remember when exactly an issue occurred, use the descriptions of the restore points for they may give you tell tale hints to a potential problem such as a recent software or driver update, etc. System restore will restore your computer directly before that event occurred and you can also undo it or try another point if your issues doesn’t go away.
Is it possible to undo changes that Windows System Restore makes?
Yes this is possible. See every time you use System Restore to restore a Windows system to a previous restore point, Windows by default will create another restore point so that you can revert back to that point in the event that the system restore action doesn’t give you your desired results. Exceptions to this rule are when you run System Restore in Windows safe mode or using the System Recovery Options. In these situations you cannot undo a restore point operation using an undo option however you can run System restore again and simply choose a different restore point if one is available.
How long are restore points saved on my system?
Windows System Restore points are saved until the disk space reserve setup under System Protection options are met. Once the reserve is met the oldest restore points will be deleted to make room for new restore points. Also if you turn off system restore, all restore points currently on your system are deleted and new restore points can only be created if system restore is turned back on. Despite turning system restore back on your old restore points prior to turning off system restore are still lost however.
Tip: You can tweak Restore Point reserve options and setup the reserve space to be as large as you want.
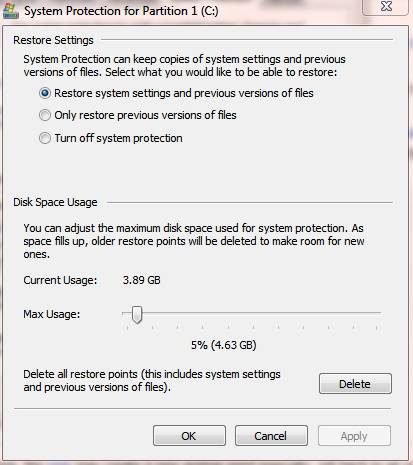
How much disk space does Windows System Restore need?
According to Microsoft, you will need at least 300MB (megabytes) of free space on any disk that is 500 MB or larger. In our experience system restore typically uses around five percent of a disks total capacity. Remember the amount of disk space System Restore uses can be tweaked. Please see the previous question for more details.
Note: System Restore will not work on an drive smaller than 1GB.
What do I do if System Restore doesn’t resolve my issue?
If restoring your computer to an earlier restore point doesn’t resolve your issue we highly recommend you undo the restore point operation or go ahead and try an older restore point. If you try all possible restore points and none resolve your particular problem we always recommend that you go back to your original point before troubleshooting with restore points began. Sometimes it can do more harm than good to revert back to a restore point if it doesn’t resolve your issue, for you may just find it gives you more issues. Instead you should look for a possible solution to your current problem elsewhere. Google, Microsoft’s website and various tech forums are a great starting place. Feel free to contact us also for we may be able to assist.
What is System Protection and how is it related to Windows System Restore?
System protection is a Windows 7 and Vista operating system feature that regularly creates and saves information about your systems files and settings. System protection also saves previous versions of files that you modified and everything is saved in restore points. Remember, restore points are created before significant modifications are performed to your system such as installing a new program or device driver. Windows System Restore points are also created automatically every seven days and you can manually create restore points any time. By default System protection is enabled for the drive that Windows 7 or Vista is installed and the drive is formatted with an NTFS partition
How to Start System Restore and Restore Your Computer to a Previous Restore Point In Windows 7 & Vista
Step 1: Click the start button and type system restore into the Windows desktop search box and then hit enter on your keyboard.
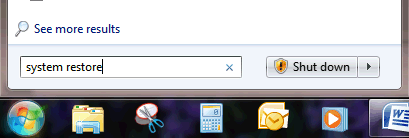
Step 2: Click next at the 'Restore system files and settings' prompt.
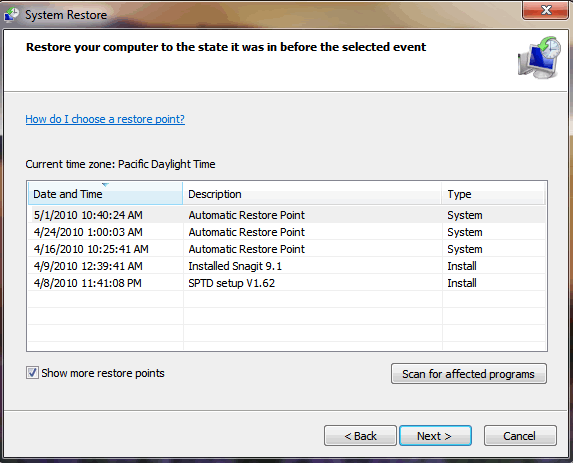
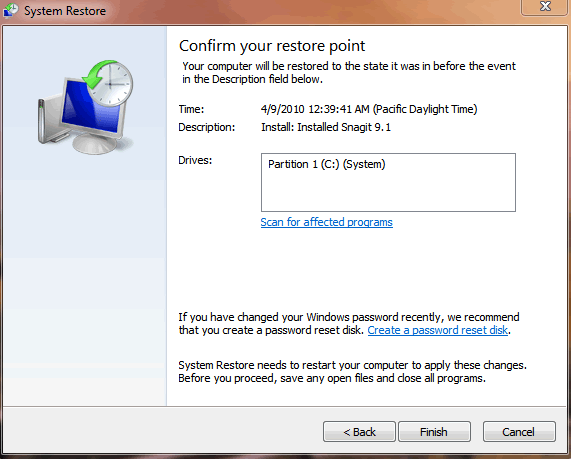
Step 3: Now select your desired restore point and click next. Clicking the box next to 'Show more restore points' will show you more possible restore points. Highlighting a specific restore point from the list and then clicking the 'Scan for affected programs' button will give you a report of which program and drivers will be deleted and which programs may not work correctly and may need to be reinstalled if you use that restore point.
Step 4: Finally confirm your restore point by reading over the details and if you are ready to proceed simply click the 'Finish' button to begin the restore point operation.
See also:
Return
from Windows System Restore Guide to Home Page
Contact us | View site map
|