Windows 7 Firewall Review & Guide
AskTheComputerTech.com - Review Series
Introducing The New Windows Firewall
The Windows 7 firewall has been revamped over Windows Vista and older versions of Windows offering new features and configuration options.
Since the beginning when the Internet Connection Firewall was introduced in Windows XP as the first firewall built into Windows operating systems, Microsoft has steadily improved the Windows firewall in succeeding versions of Windows. The Windows 7 firewall isn’t on the other hand a revolutionary step above older Windows firewalls but it is definitely a positive evolutionary step forward.
With the new Windows firewall there are some nice changes which make it a bit more user-friendly and the Windows 7 firewall also offers separate configuration settings for private networks (Home or Work) and public networks.
This for example allows laptop computers to easily connect to a remote wireless network such as at a local coffee shop without you having to tweak around with global firewall settings to achieve maximum protection.
In this review guide we are going to first dive into the new Windows 7 firewall feature set, then show you how to disable and enable the Windows firewall, allow a program through the firewall, and even configure some firewall policies.
We're also going to answer common Windows firewall questions. But before we begin, let’s set the groove and take a look at the evolutionary growth and feature set of the new Windows firewall.
If you prefer to jump to our firewall how to guide with Q&A we've provided a link at the bottom of this page. Enjoy!
The Evolution Of The Windows Firewall
Back in the days of Window XP Microsoft first introduced basic firewall software that protected you from incoming network traffic only.
Essentially only inbound connections not initiated by your computer were blocked.
On top of only basic incoming protection Windows XP versions prior to the Windows XP Service Pack 2 release didn’t even have the firewall enabled by default and administrators couldn’t even enable it via Group Policy either. Thankfully SP2 addressed these latter shortcomings.
With the introduction of Windows Vista, the Windows Vista firewall added the ability to protect against outbound network traffic in addition to inbound traffic.
Built on top of what Microsoft calls the Windows Filtering Platform (WFP), outbound traffic could be filtered via an Advanced Security Microsoft Management Console (MMC) snap-in.
Now in Windows 7 the firewall has once again been tweaked and is more user friendly than the Windows Vista firewall.
In addition to usability improvements, the firewall in Windows 7 now supports multiple active firewall policies, a perfect feature for mobile computers.
The Windows 7 firewall also brings advanced firewall settings to the forefront for easy access. In Windows Vista accessing advanced firewall settings required you to create a MMC snap-in, where in Windows 7 you can now easily access advanced firewall settings with the click of a mouse directly within the basic firewall settings Control Panel applet. See Figure 1.
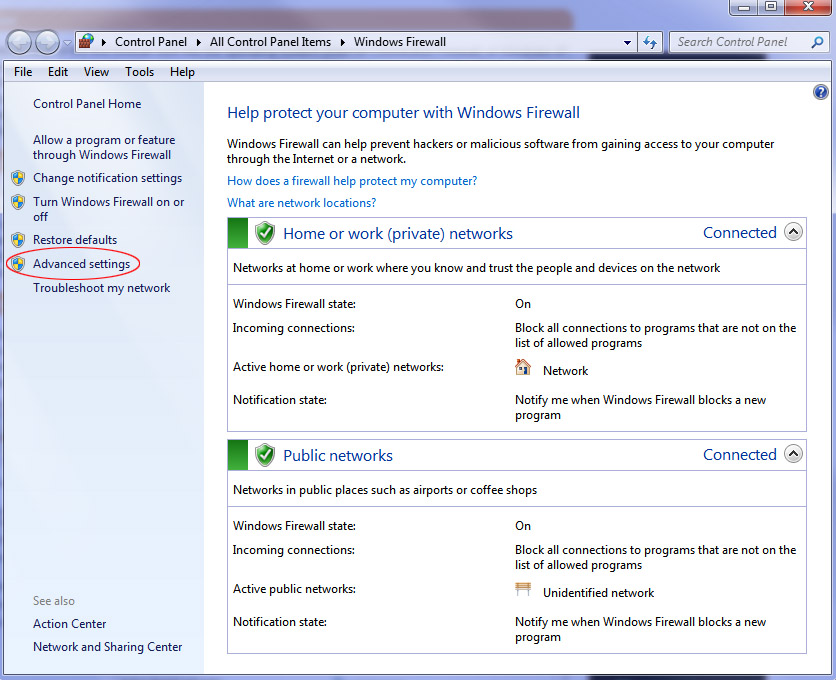
Figure 1: Windows 7 firewall settings Control Panel applet. Notice advanced settings on the left.
New Windows 7 Firewall Networking Options
The Windows 7 firewall now gives you the ability to select from three network locations types upon connecting your computer to a new network. Windows Vista in comparison only gave you the options to choose either a public or private network location type.
Selecting the home network option allows you to setup what is called a HomeGroup in which network discovery is automatically turned on allowing you to see other computers and devices on the network and them to see yours. Any of the computers that belong to the HomeGroup will easily be able to share pictures, music, videos, documents and printers. You also have the option to exclude certain folders in your document libraries if you prefer when using a HomeGroup. A HomeGroup really makes it easy to get file and print sharing setup quickly on your home network. See Figure 2.
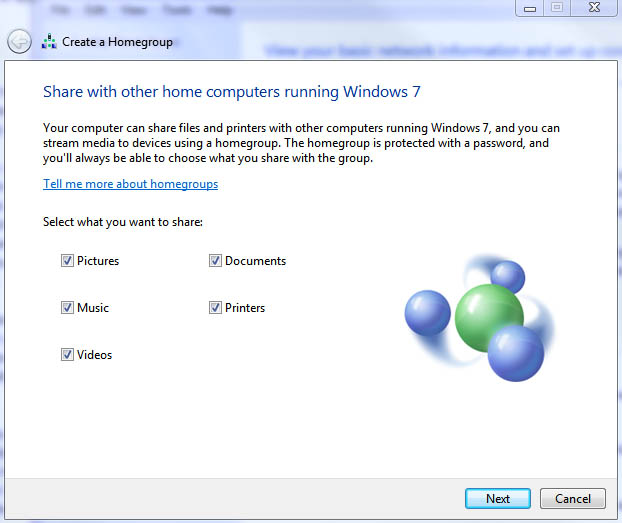
Figure 2: Creating A Homegroup
Selecting work network will turn on network discovery similar to the home network option so you will be seen on the network, though you will not be able to create or join a HomeGroup. If work network is selected and you join your computer to a domain network the Windows 7 firewall will automatically recognize and switch over to the domain network option.
Choosing Public network is perfect for when you connect a laptop to a public Wi-Fi network such as at a coffee shop, hotel or airport, or anytime you use a mobile broadband card to connect to the Internet. Public network is the most secure option and by default network discovery is turned off so other computers on the network will not be able to see you. You cannot join a HomeGroup either when you select the public network option.
A Domain network location type also exists however it is used for domain networks such as those found in a large organization, and firewall settings in this type are controlled by a network administrator and so can’t be selected or changed.
It is also worth noting that if you select any network location option the Windows 7 firewall will by default block connections to programs that aren’t on the allow/exceptions list. You can also configure settings for each network type separately if you choose such as turning the Windows firewall off or even blocking all incoming connections. See Figure 3.
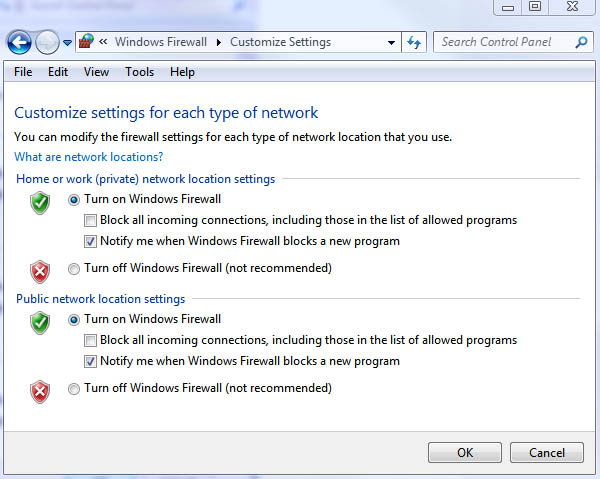
Figure 3: Customize Windows 7 Firewall settings for each type of network
Windows 7 Firewall Network Location Types Overview:
- Home Network: Select Home network for home networks or when you know and trust the people and devices on the network. Computers on a home network can also belong to a HomeGroup. By default network discovery is turned on for home networks. Network discovery is the piece that allows you to see other computers and devices on the network and it also allows other network users to see your computer.
- Work Network: Select Work network for a small office or other workplace network. By default network discovery is turned on for work networks similar to the home network option however unlike the home network option you cannot join a HomeGroup.
- Public Network: Select Public network for networks in public places such as coffee shops, hotels, airports, and any other public network where unknown systems may be connected. This location type is designed to keep your computer from being visible to other computers around you and to also help protect your computer from malicious software (malware) from the Internet. Similar to the work network option you cannot select a HomeGroup, however unlike the work network option network discovery is turned off by default. The public network option is highly recommended anytime you connect to an unknown network, if you are connected directly to the Internet without using a router, or if you have a mobile broadband connection.
- Domain Network: The Domain network location is used for domain networks such as those found in a large organization. The domain network location type is controlled by a network administrator and can't be selected or changed.
Windows 7 Firewall Active Profiles
Another evolutionary step in the Windows 7 firewall is its support for multiple firewall profiles simultaneously. While Windows Vista had multiple profiles for both public and private networks too, it differed in that only one could be active at once.
With the Windows 7 firewall you can now be connected to multiple networks simultaneously with each network connection running through a different firewall profile giving it more flexibility in certain situations. In Vista for example firewall settings were global so if you had multiple network connections both would be restricted through a single firewall profile.
As an example, let's say you are running Windows Vista and wanted to connect to more than one network such as a public and private network at the same time. You may not be able to perform a certain action on the local (private) network when you are running under firewall rules for the public network or vice versa because all traffic is governed by a single filewall profile. The Windows 7 firewall solves this problem by allowing each network adapter to operate under a different profile.
Windows 7 multiple active firewall profiles are really going to benefit individuals who are connected to two different networks at the same time with a need for different firewall configuration settings on each network connection. One network adapter can now operate under rules for a private network and the other network adapter can operate under the rules for the public.
Configuring Windows Firewall Profiles with Advanced Security
Configuring network profiles options can easily be performed by using the Advanced Settings console. See Figure 4.
Various Options that can be configured for each profile:
- Firewall State: (Set on/off status of the Windows firewall)
- Inbound connections: (block, block all connections, or allow)
- Outbound connections: (allow or block)
- Display notifications: (yes or no, whether or not to notify you when a program is blocked)
- Allow unicast response: (yes or no, to multicast or broadcast traffic)
- Apply local firewall rules: (yes or no, created by the local administrator in addition to Group Policy firewall rules)
- Allow local connection security rules: (yes or no, created by local administrators in addition to Group Policy connection security rules)
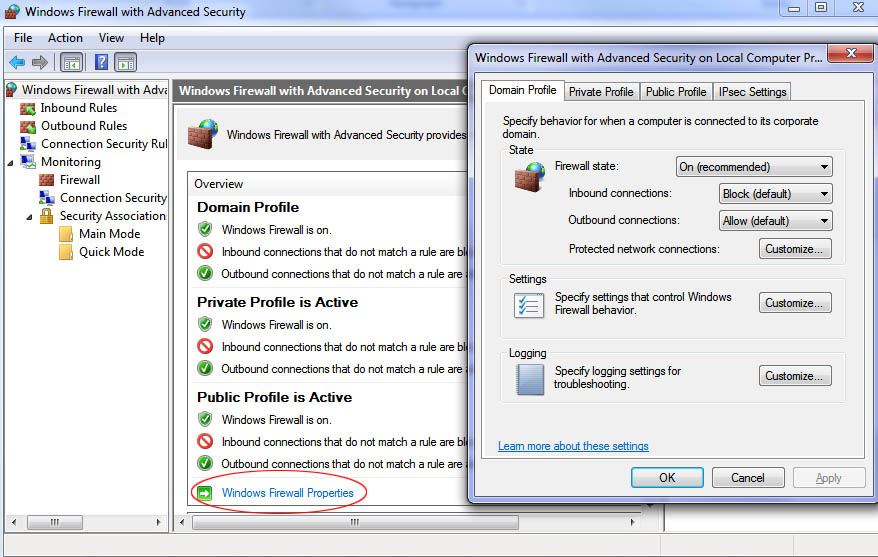
Figure 4: Configuring options for firewall profiles with Advanced Settings
Subtle Windows 7 Firewall Tweaks
The new Windows firewall also supports subtle changes and usability tweaks that make it more user-friendly too, especially for system administrators.
One new feature we really like is the ability to specify ranges for port numbers and IP addresses when creating firewall rules. If you find yourself tweaking with firewall rules this can save you a whole lot of time. In Vista it was rather cumbersome to list port numbers and IP addresses individually.
For more advanced Windows firewall administration, creating connection security rules to specify which ports or protocols are subject to Internet Protocol security (IPsec) requirements can now easily be done in the firewall console. To perform the same action in the Windows Vista you had actually to use the “netsh” command line utility.
Another nice enhancement in the Windows 7 firewall is the Windows Firewall With Advanced Security piece in the Event Viewer. Previously in Windows Vista the Windows firewall could be configured to log events in a log file located in the C:\Windows\System32\LogFiles\Firewall\pfirewall.log) folder, however now in Windows 7 firewall events are also logged in the Event Viewer making access much easier.
Launching the log is as simple as opening the Event Viewer and browsing via the left hand pane to Applications and Services Log>>Microsoft>>Windows>>Windows Firewall with Advanced Security. See Figure 5.
These and other small enhancements are definitely welcoming changes in Windows 7. Microsoft has done their homework this time around and have certainly approved upon the ever evolving Windows firewall.
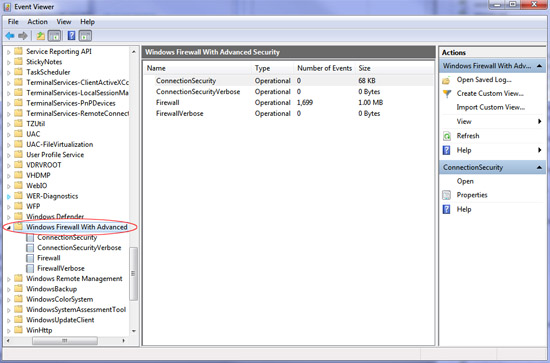
Figure 5: Viewing Windows 7 firewall logs in the Event Viewer
Conclusion:
We feel the Windows 7 firewall does a pretty nice job at protecting your computer on a network, and with the subtle yet functional changes Microsoft has made the Windows firewall has again taken a step forward in Windows security protection. So while the changes are not exactly revolutionary gains over Windows Vista, they are most definitely a positive step forward and we're happy Microsoft has been doing their homework.
Have additional Windows 7 firewall questions? Ask the computer tech now!
See also:
Return
from Windows 7 Firewall Review & Guide to Home Page
Contact us | View site map
|