Windows 7 Msconfig Startup Utility Guide
This guide also applies to Windows Vista and the concepts in this guide also work with earlier Windows versions.
Windows 7 Msconfig Startup Utility Overview, Tips, & More
The Windows Msconfig startup utility is a very handy tool that was primarily designed to help you identify problems that may be preventing Windows 7 and other Windows operating systems from starting correctly.
System Configuration is the actual Microsoft application name for Msconfig but the terms are used interchangeably being that Msconfig is the command you input to launch the utility. The term Msconfig however is more often used in the IT world when referencing the utility but just be in the know for you may hear both terms.
The Msconfig startup utility is one of those must use utilities that every IT support person will benefit from when troubleshooting Windows 7 startup problems.
In fact, the Msconfig startup utility has been in Windows operating systems for some time helping IT folks troubleshoot Windows startup issues.
Older versions of Windows may have slightly different Msconfig options though the utility is pretty darn similar across the board. Windows Vista, XP, and some other versions of Windows include Msconfig.
Information Technology support individuals often also use the Msconfig startup tool to quickly streamline a computer’s resources by removing unneeded apps from starting. Since apps running in the background after startup use up memory and CPU processing cycles, removing them can help a computer run better, especially useful for older computers with less memory and processing power.
Home users alike will also love the Msconfig startup utility for it the perfect tool to tweak a new home PC, allowing you too quickly and easily stop pre-installed manufacturer software (crap-apps) from starting every time you log into your computer.
On the other hand, the Msconfig/System Configuration utility was primarily designed to find and isolate startup problems opposed to being used as a startup management program.
In a fast paced IT support role technicians often use the Msconfig startup utility to quickly optimize a system by preventing a service/app from starting, but if applicable it is much better to permanently remove an app by uninstalling it over simply stopping a service/app from launching.
By uninstalling an application entirely, it removes not just startup services/apps from running but the entire application itself thus freeing up disk space and even potentially preventing application compatibility issues down the road. Check out Microsoft’s Uninstall or change a program guide if you are new to removing applications from Windows.
Troubleshooting startup problems with the Msconfig startup utility is a snap. First use Msconfig to configure Windows to start with common services and startup programs turned off. If your startup problems go away after turning off these common services/startup programs then proceed to turn them back on one at a time until the system problem you were experiencing reoccurs. If a problem does not occur when a service is turned off but it does occur when the same service is turned on then most likely you found the cause of the startup problem. Nice and easy!
As you see, the Msconfig startup utility is a very handy tool for troubleshooting Windows 7, Windows Vista, Windows XP, Windows 98 and other Windows operating system startup problems. It is also a fast way to streamline a computer’s resources by preventing an application or service from starting.
Windows 7 Msconfig Startup Utility Options Overview
Msconfig Startup Utility - General Tab Overview:
The Msconfig startup utility General tab lists various startup configuration modes available for troubleshooting Windows startup issues.
- Normal startup: Starts Windows normally. This loads Windows with all programs and services. This mode is the default mode.
- Diagnostic startup: This mode starts Windows 7 with basic services and drivers only. It is useful if say you want to rule out basic Windows files as a potential problem.
- Selective startup: Selective mode starts Windows 7 with basic services and drivers like diagnostic startup mode though it also starts programs you select.
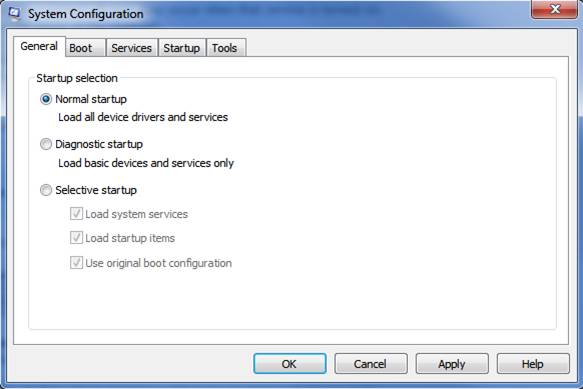
Msconfig Startup Utility - Boot Tab Overview:
The Msconfig startup utility Boot tab shows you various configuration options for Windows 7 and advanced debugging settings that include:
- Safe boot: Minimal: On startup this mode launches Windows in safe mode using the Windows graphical user interface (GUI) with only critical system services running. Networking is also disabled in this mode.
- Safe boot: Alternate shell: Upon startup this mode opens the Windows command prompt in safe mode with only critical system services running. In this mode both networking and the graphical user interface (GUI) are disabled.
- Safe boot: Active Directory repair: This mode opens the Windows graphical user interface in safe mode running critical system services and Active Directory.
- Safe boot: Network: On startup this mode launches Windows in safe mode using the Windows graphical user interface (GUI) with only critical system services running. Networking is enabled in this mode.
- No GUI boot: This prevents the Windows Welcome screen from displaying upon starting.
- Boot log: This stores all information from the startup process in the file %SystemRoot%Ntbtlog.txt.
- Base video: This mode opens the Windows graphical user interface (GUI) using a standard VGA graphics driver instead of display drivers specific to the video card on your computer.
- OS boot information: This will show you driver names as drivers are being loaded during the Windows startup process.
- Make all boot settings permanent: If enabled changes made in the System Configuration utility aren’t tracked. Options can be tweaked later using System Configuration but they must be changed manually. When this option is selected you also cannot roll back your changes by simply selecting Normal startup on the General tab.
The Advanced boot options button within the boot tab gives you additional control over Windows startup. These options are typically for advanced startup troubleshooting or development work and so most users will never tweak these settings:
- Number of processors: You can use this to limits the number of processors used on a multiprocessor system.
- Maximum memory: With this option you can specify the maximum amount of physical memory in megabytes (MB) to be used by the operating system. This is useful if you want to simulate a low memory configuration.
- PCI Lock: PCI Lock prevents Windows from reallocating input/output (I/O) and IRQ resources on the Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) bus and so the I/O and memory resources set by the BIOS are preserved.
- Debug: This enables kernel-mode debugging for device driver development. This option is more for development work and not something an end user would honestly use.
- Global debug settings: Allows you to specify debugger connection settings on the computer so a kernel debugger can communicate with a debugger host. The debugger connection between the host and target computers can be a Serial, Firewire (IEEE 1394), or USB 2.0 connection.
- Debug port: Specifies using Serial as the connection type and the serial port. The default port is COM 1.
- Baud rate. An optional setting that allows you to specify the baud rate to use when a Debug port is selected and the debug connection type is Serial. Valid values for baud rate are 9600bps, 19,200bps, 38,400bps, 57,600bps, and 115,200bps. The default baud rate value is 115,200 bps.
- Channel. Specifies using IEEE 1394 as the debug connection type and specifies the channel number to use. The value for channel must be a decimal integer between 0 and 62, inclusive, and must match the channel number used by the host computer. The channel specified does not depend on the physical IEEE 1394 port chosen on the adapter. The default value for channel is 0.
- USB target name. Allows you to specify any number for a string value to use when the debug type is USB.
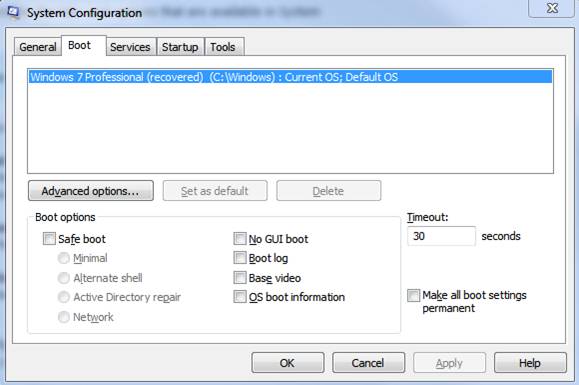
Msconfig Startup Utility - Services Tab Overview:
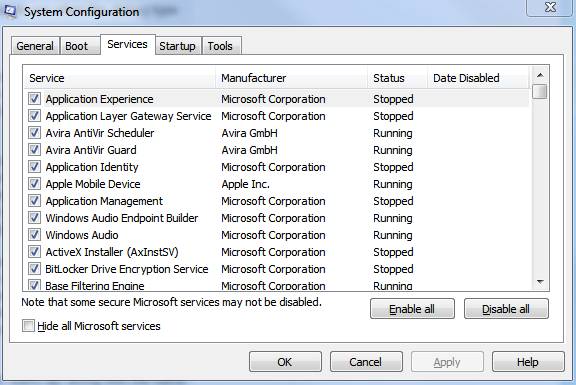
The Services tab lists all of the services that start when your computer starts along with each services current status. As service will be listed as either running or stopped. This tab is useful if you want to enable or disable specific services at startup to troubleshoot if a specific service is causing a startup problem.
If you select “Hide all Microsoft services” this will only show third-party applications in the services list. This is a useful option because more often it is a third-party service that is problematic and so it makes it easy to isolate and diagnose them. Simply uncheck a service and the next time you restart your computer that service will not launch. Note: If you chose Selective startup on the General tab you must either choose Normal startup on the General tab or manually recheck a services check box if you want to start it again. Pretty straight forward!
Best Practices: Take caution when disabling services using the Msconfig startup utility for disabling the wrong service can possibly cause system instability and/or some programs may stop functioning correctly or even launch. See some apps rely on specific services to function correctly so it is a best practice to only disable a service if you know for certain that it isn’t an essential service. Of course if you disable the wrong service you can always re-enable it. Note: If you select “Disable all” some core Microsoft services required for the operating system to start will not be disabled.
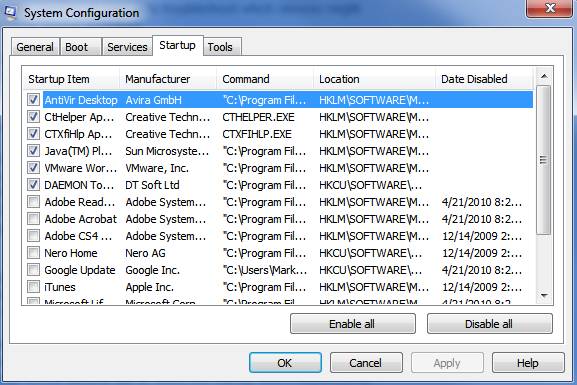
Msconfig Startup Utility - Startup Tab Overview:
The Startup tab is one of the more commonly used tabs by IT support specialists. It allows you to quickly disable and prevent an application from starting when Windows starts. As we mentioned in our Msconfig startup utility introduction, this is the tab that you use to isolate potentially problematic startup programs, or to quickly streamline a system by removing unneeded applications from running.
The Startup tab lists applications that run when your computer starts, the name of the manufacturer, the path to the files executable file, the location of the registry key or shortcut used to launch the application, and additionally it will show you when a startup item was disabled as seen in our screenshot.
Using the Startup tab is as simple as un-checking an application that you don’t want to load when Windows starts. Uncheck an app and simply reboot your computer for changes to take effect. Note: If you chose Selective startup on the General tab you will need to choose either Normal startup on the General tab or recheck the application under the Startup tab to re start the application.
Best Practices: Similar to working in the Services tab, it is best to disable startup applications only if you are sure they won’t compromise an application from running correctly. Some applications may rely on an application to launch at startup, etc. and if disabled that application may behave unexpectedly. When in doubt leave a program enabled but worst case scenario if you notice an application doesn’t work correctly after you’ve disabled something, simply go back into the Windows 7 Msconfig startup utility and re-enable accordingly.
Here is a link to a database of Startup applications which you may find useful. If you are unsure if you need a specific application you may find it here. http://www.sysinfo.org/startuplist.php
How to launch the Windows 7 Msconfig startup utility:
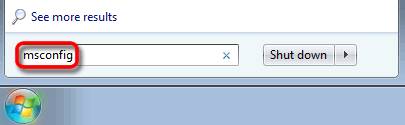
Click on the Windows 7/Vista start menu icon in the bottom left corner of your screen and then in the search box simply type msconfig and hit enter on your keyboard as shown in the screenshot. Older versions of Windows simply type msconfig in the run box to quickly launch the Msconfig startup utility.
See also:
Return
from Windows 7 Msconfig Startup Utility to Home Page
Contact us | View site map
|