The Birth Of Modern Day Computers
Modern Day Computers - The Evolution
 All modern day computers are in a nutshell a collection of electronic switches. Switches are used to represent and control the routing of data in the form of binary digits or sometimes just called bits. Binary information is represented by on and off states and because of this an efficient electronic switch is required. All modern day computers are in a nutshell a collection of electronic switches. Switches are used to represent and control the routing of data in the form of binary digits or sometimes just called bits. Binary information is represented by on and off states and because of this an efficient electronic switch is required.
Think of the way you turn a light switch on and off. Say you took a regular light switch and turned it on, off, and then on one more time. Then again turn it on, off, on, on, off. Hypothetically let’s say the first combination of on and offs means yes and the second combination of on and offs means no. Make sense? Basically we’ve just used a light switch by turning it on and off to represent words.
In the early days of electronic computers they used vacuum tubes as switches. Vacuum tubes did however come with a fair share of problems. The type of tube used in early computers was called a triode. As you learned in our computer history timeline the triode was invented in 1906 by Lee De Frost. Basically this triode consisted of a cathode and a plate that was separated by a control grid and suspended in a glass vacuum tight tube.
This cathode is heated by a red hot electrical filament and it emits electrons that are then attracted to the plate. In the middle of all this lies the control grid which is used to control the flow of all the electrons. By making it positive they are attracted towards the plate and by making it negative all the electrons are repelled back to the cathode. Basically you control the grid current to in turn control the on and off output of the plate. Pretty cool!
Unfortunately like we briefly mentioned the tube was very inefficient as a switch, mainly because it consumed tons of electrical power and additionally it generated a huge amount of heat. This caused significant problems in early systems and because of the heat tubes were very unreliable and often failed every few hours give or take.
Modern Day Computers – The Invention of the Transistor
 The invention of the transistor or semiconductor was probably the most important development that lead to the personal computers amazing growth and what we know of as modern day computers. The invention of the transistor or semiconductor was probably the most important development that lead to the personal computers amazing growth and what we know of as modern day computers.
In 1947 the first transistor was invented by two engineers working for Bell Laboratories named John Bardeen and Walter Brittain.
Also and only a few months after Bardeen and Brittain’s transistor William Shockley from Bell invented a junction transistor. In 1956 all three together shared the Nobel Prize in Physics for their invention of the transistor. What an amazement accomplishment it was.
The transistor ultimately replaced the vacuum tube as an electronic switch because it was so much smaller and less power hungry. Let’s not forget computer systems built around the transistor were also smaller, faster, and way more efficient than vacuum tube designs.
Modern Day Computers – The Makeup of the Transistor
Transistors are primarily composed from the two elements silicon and germanium. Some impurities are also added and depending on which impurities and its electron content the material becomes what is called N-Type/negative, or P-Type/ positive. Both N-Type and P-Type are conductors and so they allow electricity to flow in either direction. If you join the two on the other hand a barrier in the middle is formed and electrical current flows only in one direction when the voltage is present in the correct polarity, hence the name semiconductors.
Transistors are made by placing two P and N junctions back to back and by squeezing a thin wafer of one type of semiconductor material between two wafers of the other type. Wafers in the middle made from P-Type are called a NPN and those of N-Type are called PNP.
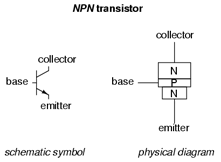 When discussing NPN transistors the N-Type semiconductor material on one side of the wafer is designated an emitter and it is most often connected to a negative electrical current. The P-Type material in the middle is the base, and finally the N-Type material on the other side of the base is called the collector. When discussing NPN transistors the N-Type semiconductor material on one side of the wafer is designated an emitter and it is most often connected to a negative electrical current. The P-Type material in the middle is the base, and finally the N-Type material on the other side of the base is called the collector.
If you compare an NPN transistor to a vacuum tube triode the emitter is actually the equivalent of the cathode, the base is the same as the grid, and finally the collector is the tubes equivalent of the plate component. Simply control the current at the base and it actually controls the flow of electrical current between the emitter and collector. Pretty sweet!
Long gone are the days of the tube as you can see, the transistor is simply way more efficient and it can be shrunk to microscopic proportions. Today’s microprocessors such as the Core 2 Duo and others literally have millions of these microscopic switches we call transistors. Pretty amazing!
Return to:
Return
from Modern Day Computers to Home Page
Contact us | View site map
|